Twitter Analytics on Companies, Executives, and COVID-19
29 Nov 2021
Dr. Richard M. Crowley
rcrowley@smu.edu.sg
https://rmc.link/ \(\cdot\) @prof_rmc
Twitter Analytics on Companies, Executives, and COVID-19
29 Nov 2021
Dr. Richard M. Crowley
rcrowley@smu.edu.sg
https://rmc.link/ \(\cdot\) @prof_rmc
Firm tweets
“Discretionary Dissemination on Twitter”
With Wenli Huang and Hai Lu
Questions
- Firms post financial tweets more often around more material accounting news events, irrespective of the direction of the news (positive or negative)
- Testing theory: Hummel, Morgan, and Stocken (2018 Working)
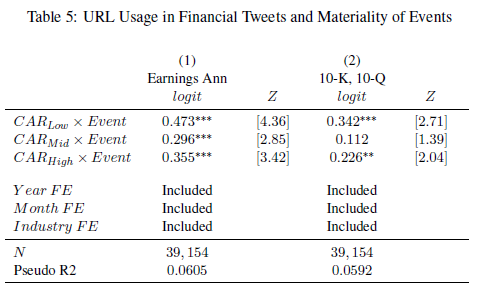
- Firms use hyperlinks more often around more material accounting news events, irrespective of the direction of the news (positive or negative)
Example firm financial tweets
Financial
GS reports 2014 net rev of $34.53bn, net earnings of $8.48bn, & 11.2% ROE; 4Q net rev of $7.69bn, net earnings of $2.17bn and 11.1% ROE
— Goldman Sachs (@GoldmanSachs) January 16, 2015
Boeing reports strong third-quarter results; raises revenue, EPS and cash flow guidance: https://t.co/Pedat1dDJo
— The Boeing Company (@Boeing) October 21, 2015
Non-financial
Tip: Your front door is a glimpse into your home. Add some personality. After all, you only have one chance to make a first impression!
— LendingTree (@LendingTree) September 8, 2014
Are you thinking #FiveYearsOut? Then you should consider working with us. Apply online at http://t.co/nq5llQlyuG pic.twitter.com/uHeWBZhmA4
— Arrow Electronics (@ArrowGlobal) March 6, 2015
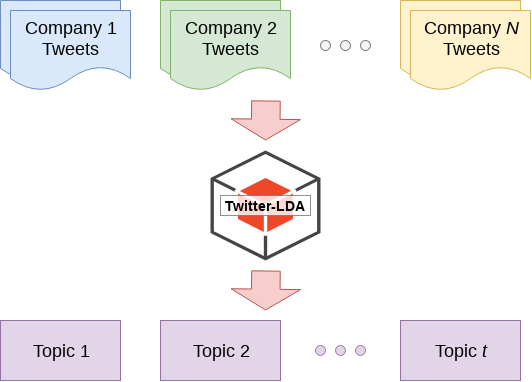
Classifying tweets
- Classify using Twitter-LDA
- Identify 60 topics
- 1 financial topic
- 42 nonfinancial topics
- Business, conferences, marketing, and support
- 17 other topics
| Number | Topic | Top_words |
|---|---|---|
| 23 | Financial | market, growth, markets, trading, earnings, global, report, quarter, results, energy |
| 2 | Nonfinancial: Marketing | #shareacoke, make, #tastethefeeling, gifs, reply, mistletoe, happy, tweets, #makeithappy, hashtag |
| 12 | Other | el, paso, police, trump, obama, man, city, donald, news, york |
Tweeting behavior intraday

Financial tweets and Financial events
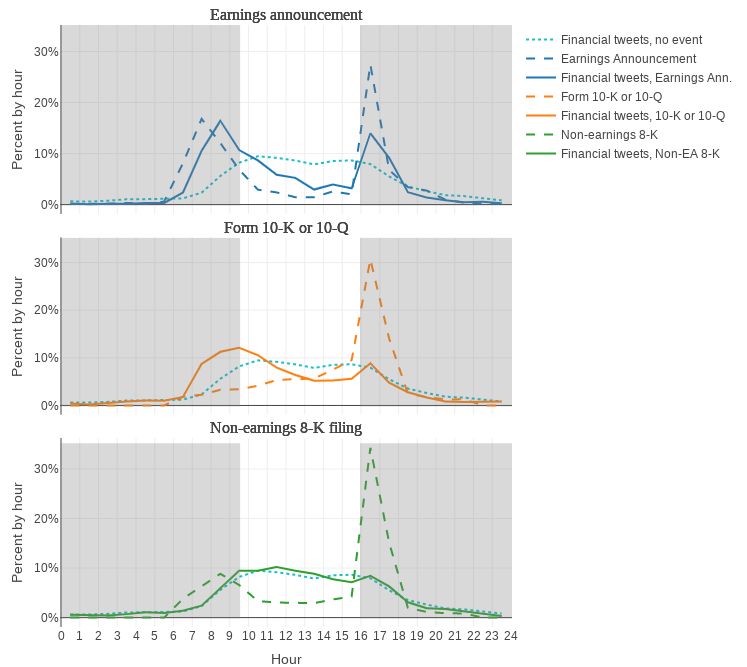
Financial tweets and event direction

Financial tweets and url usage
CEO and CFO tweets
“Executive tweets”
With Wenli Huang and Hai Lu
Research Questions and hypotheses
- What drives exec adoption of Twitter?
- Do executives view Twitter as an important channel for disclosure?
Hypotheses:
- The market responds to executive financial tweets in addition to firm tweets.
- The market responds more weakly (strongly) to executive tweets with content similar to firm tweets.
- Weakly: new information mechanism, the market reacts to new information content posted by executives
- Strongly: trust mechanism, the market reacts due to stronger social bonds with individuals than firms
Example exec tweets (Business)
Financial
Continuing to execute in both our product & SG&A cost reduction initiatives will provide consistent EPS leverage #MDTEarnings
— Omar Ishrak (@OmarIshrak) February 19, 2013
Good summary of our recent quarterly earnings call: http://t.co/Qn0TapmLmT.
— Matt Desch (@IridiumBoss) August 2, 2014
Nonfinancial
Arriving in Atlanta. A day meeting with customers is better than any day in the office. But I do love all the folks back in Hartford too :o)
— Mark T. Bertolini (@mtbert) February 27, 2012
Giving keynote tomorrow at #inside3DPrinting Talking about the good, bad of #3Dprinting and the future of software
— Carl Bass (@carlbass) April 4, 2014
Example exec tweets (Other)
Hail #uncool Mother Nature showing her fury pic.twitter.com/HWqQa6tK57
— Tony Thomas (@TonyThomasWIN) April 20, 2015
Another great day of spring skiing in the Alps pic.twitter.com/DhySN4hSud
— Carl Bass (@carlbass) April 10, 2014
Tweet content over time
Executive Adoption of Twitter

Adoption is higher when younger, female, extroverted, or facing higher litigation risk. SEC’s 2013 guidance lowers adoption rate at high litigation risk firms.
Executives’ Discretionary Tweeting

Executives seem to view Twitter as an important disclosure channel
Executives Drive Stock Returns

Executives’ financial tweets lead to investor reaction beyond that of firms
Market Reaction Mechanism: Trust
\[ \scriptsize \begin{array}{l c c} \hline & \text{During trading hours} & \text{Before trading hours} \\ \text{Variable} & \left|MMR_{t}\right| & \left|MMR_{t}\right| \\ \hline \text{Fin tweets, Exec} & -0.025^{**} \\ & (-2.22) & \\ \text{Fin tweets, Exec} \times \text{Similarity} & 0.074^{**} \\ & (2.26) & \\ \text{Fin tweets, Exec} \times \text{No firm tweets} & 0.026^{**} \\ & (2.35) & \\ \text{Fin tweets, Exec} & & -0.014^{***} \\ & & (-3.17) \\ \text{Fin tweets, Exec} \times \text{Similarity} & & 0.046^{***} \\ & & (3.30) \\ \text{Fin tweets, Exec} \times \text{No firm tweets} & & 0.017^{***} \\ & & (3.41) \\ \text{Controls; Firm, Exec, Year, Month FE} & \text{Yes} & \text{Yes}\\ \hline \end{array} \]
Result is consistent with Trust driving investor reaction to exec financial tweets.
Methodology: Trust vs Information
We identify how content-wise similar each exec tweet is to corresponding firm tweets via Universal Sentence Encoder (USE).

USE is a neural network method that relies on word meaning and word order to determine sentence meanings. It does not rely on word choice.
USE example
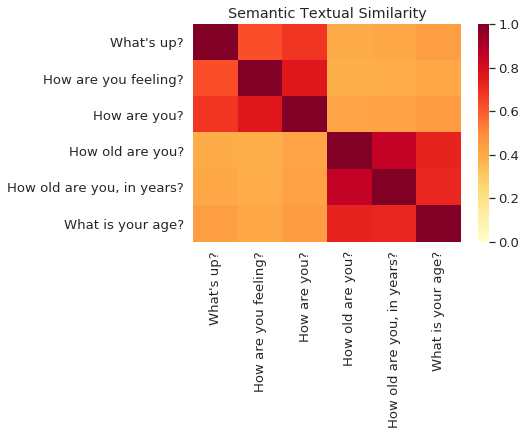
USE abstracts away from word choice!
COVID-19 tweets
WIP with Hai Lu and Jee-Eun Shin
Large scale data exercise
- This project is pushing into “Big Data” territory
- 2+ billion messages gathered
- 25+ languages
- 190+ countries, territories, and regions
Project’s goal
- To understand, at a macro level, why some economies reopen and others don’t, based on the local sentiment
- To understand the impact of local sentiment on economic activity post-reopening
Reopening vs other discussion
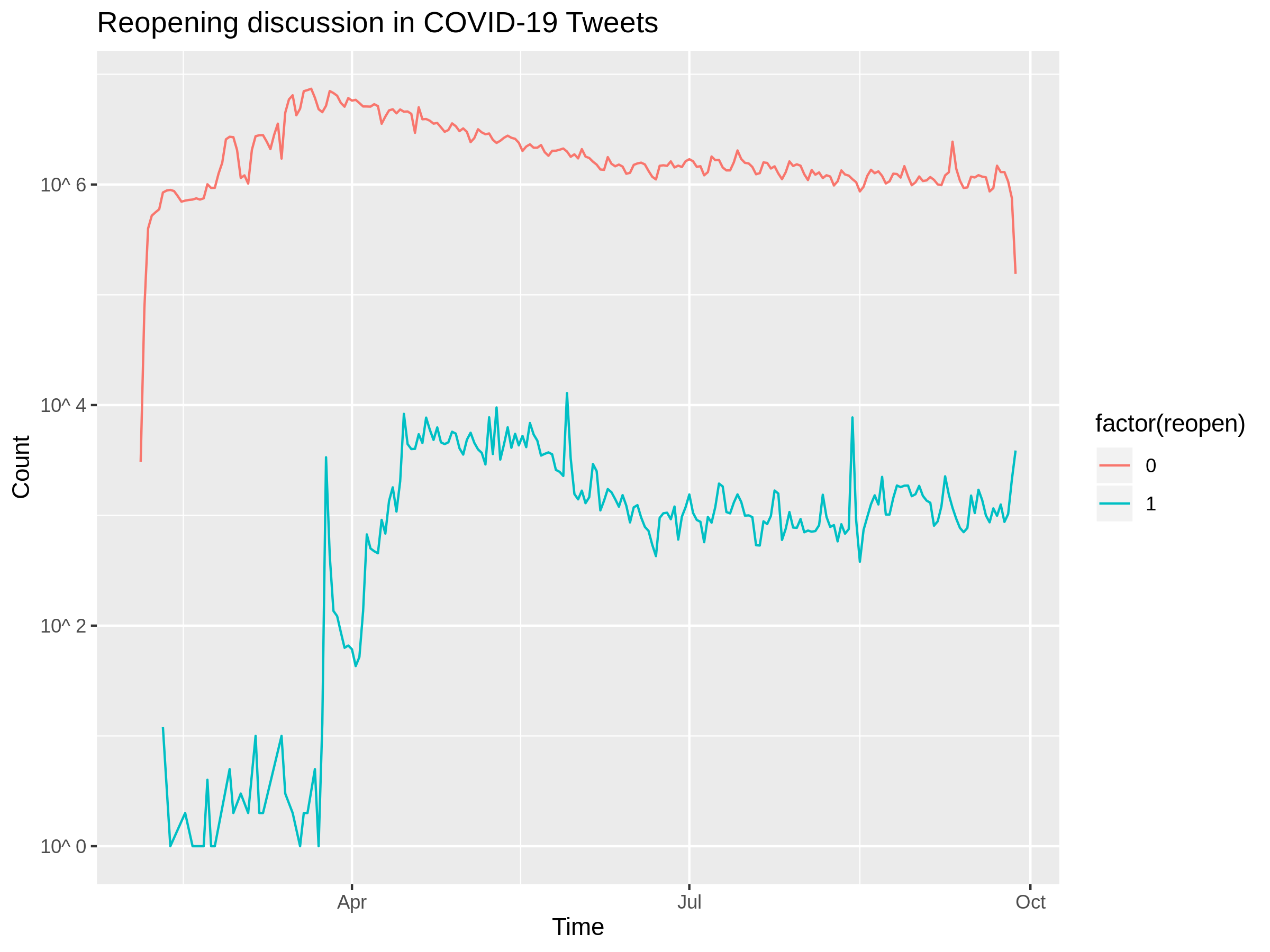
Applications of broad measures to accounting
How does a populace’s emotion about reopening with COVID impact economic recovery?
- Examine tweets to capture emotion at fine-grained geographic and temporal scales
- State-day level variation in fear, sadness, anger, joy, and surprise
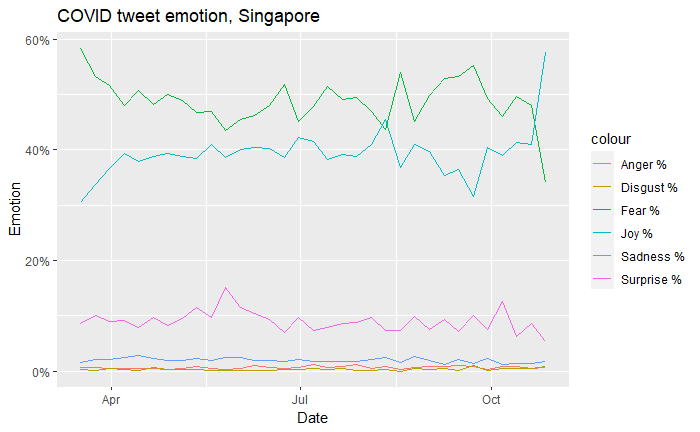
Mask depiction and emotions
- Tweets:
- Feb-Oct 2020
- Singapore-based users
- English language text
- Hashtag about COVID in the text
Over 13,000 images in this sample that include people in them
- Use computer vision to pick out masks
- 3 class model: no mask, mask, or mask worn improperly

- E.g., per the model, the guy on the left has his mask on incorrectly
In SG, those that post pictures of people wearing masks properly exhibit ~5% less fear than those that post people without masks on (\(t=586\))
Wrap Up
Conclusion
- From an accounting perspective…
- Non-traditional information sources are common to use
- Companies are using Twitter to great effect for informing investors
- Symmetrically disclosing both good and bad news
- Executives have substantial impact when disclosing financial information on Twitter
- Due to investors’ trust of the executives
- From a macro perspective
- Sources of public information such as Twitter provide an interesting set of insights into the reaction of individuals
We can leverage social media to understand macro phenomena or the environment micro-econ phenomena occur in
Questions?
Dr. Richard M. Crowley
rcrowley@smu.edu.sg
https://rmc.link/ \(\cdot\) @prof_rmc
Packages used for these slides
- dplyr
- ggplot2
- gridExtra
- kableExtra
- knitr
- revealjs
NOTES
- Won’t be displayed ever
